Wavelength
Wavelength is the distance from the start of one wave to the corresponding point on the next wave. You can find wavelength by measuring from one crest to the next or from one trough to the next. The units of wavelength are usually meters but can be any unit of length. The visible light spectrum has a wavelength that ranges from roughly 6.2×10-7 meters to
4×10-7 meters.

Frequency
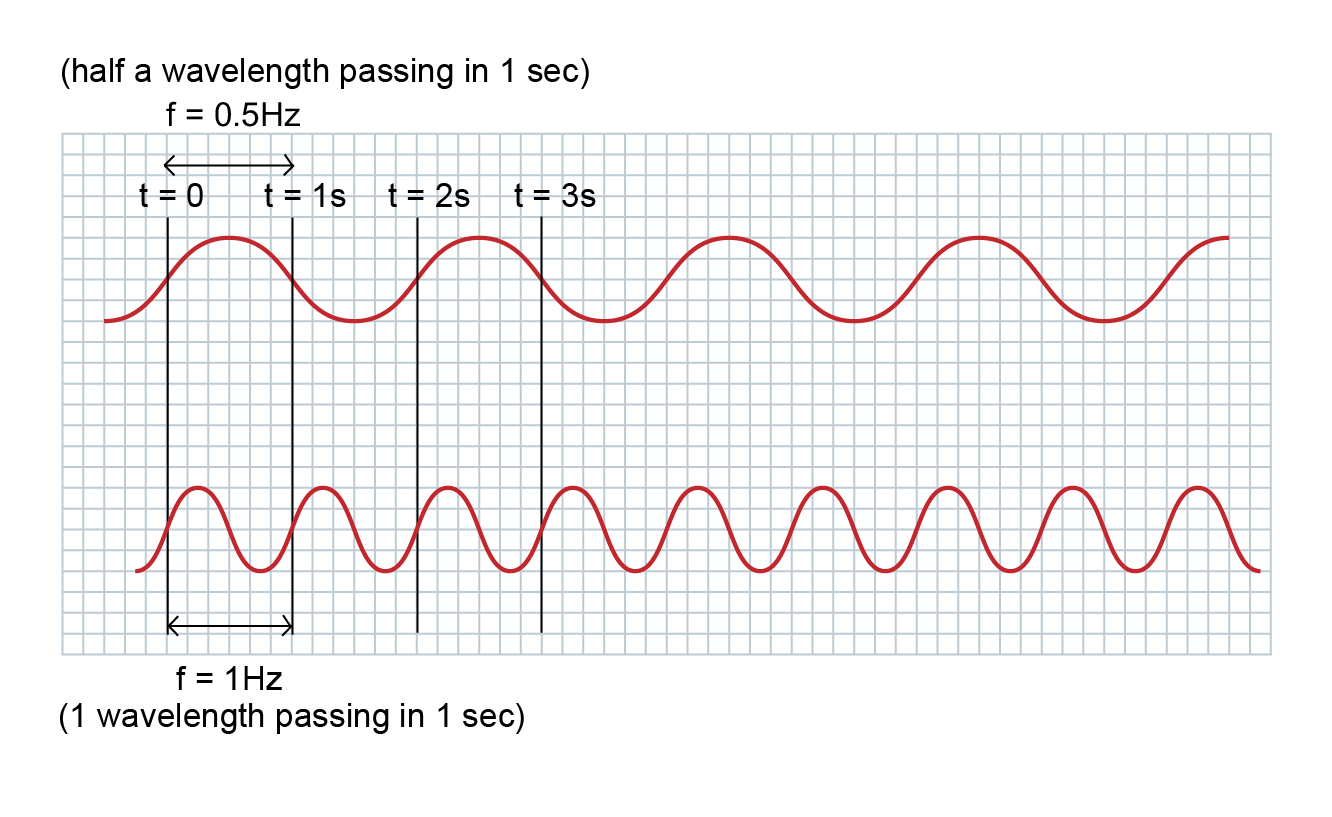
Frequency is the number of full waves that pass by in a certain time interval. You can find the frequency by counting the number of full waves that pass by in 1 second. The units of frequency are hertz (Hz). Waves with a long wavelength will have a low frequency and waves with a short wavelength will have a high frequency.
Wavelength Measurement
Use the grid or the ruler to measure the wavelength of the waves. Enter the lengths into the fields and submit the answers.

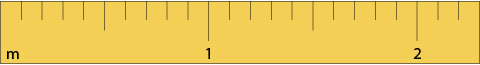
1 grid = 0.1 meters
meters

meters


meters


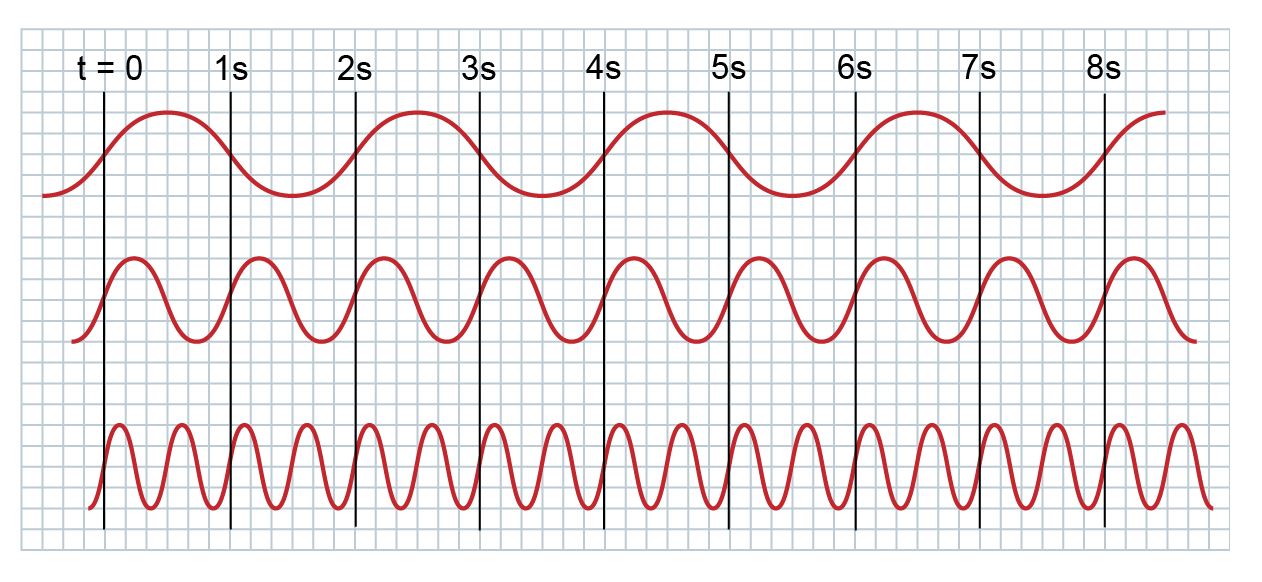
Frequency Measurement
Use the grid to help you measure the frequency of the waves. Enter the frequency into the fields and then submit your answers.
Hz


Hz


Hz


Move the slider to view EM (electromagnetic) wavelengths and interesting facts about individial radiations.
Radio waves
Radio waves are used for communication. They can travel long distances, including from the farthest reaches of the visible universe.
Wavelength ( λ )
Very long to 1×10-2 m
Frequency ( f )
Very few to 3×1010 Hz
Microwaves
Microwaves are used for cell phone communication and cooking. When you put your food in the microwave the water molecules in the food absorb the energy from the microwaves and heat your food.
Wavelength ( λ )
1×10-2 m to 1×10-3 m
Frequency ( f )
3×1010 Hz to 3×1011 Hz
Infrared (IR)
Infrared light is given off by all objects that are above zero kelvin. Night vision cameras work by sensing the infrared light and creating an image where hot areas are light and cooler areas are dark.
Wavelength ( λ )
1×10-3 m to 6.2×10-7 m
Frequency ( f )
3×1011 Hz to 4×1014 Hz
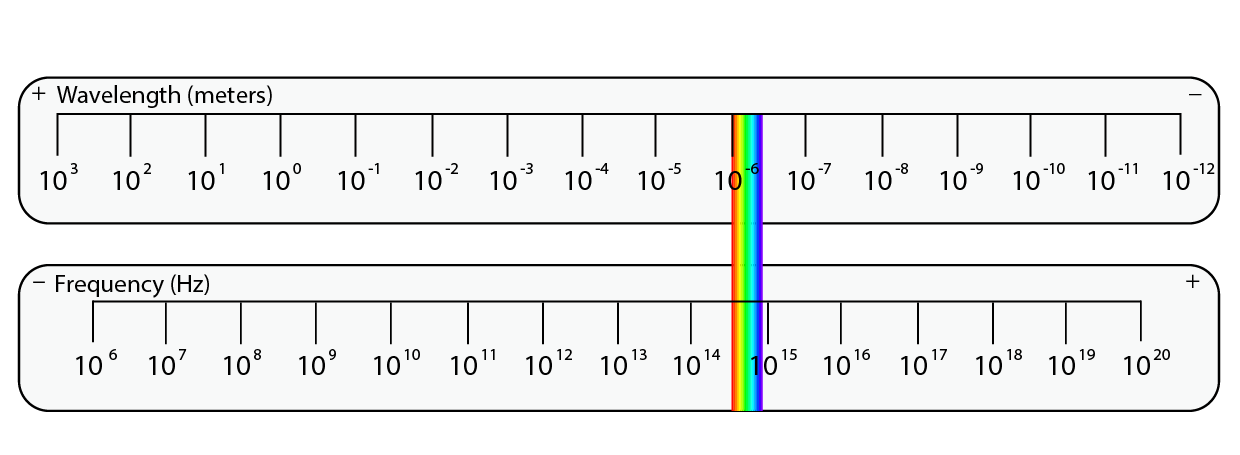
Visible light
Visible light is the only part of the electromagnetic spectrum humans can see. As you go across the rainbow of colours from red to violet, the wavelength gets shorter and the energy gets higher.
Wavelength ( λ )
6.2×10-7 m to 4×10-7 m
Frequency ( f )
4×1014 Hz to 7.5×1014 Hz
Ultraviolet (UV rays)
UV light rays are the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that causes skin to tan or burn. It also stimulates vitamin D production in the body and can be used to sterilize medical instruments.
Wavelength ( λ )
4×10-7 m to 1×10-9 m
Frequency ( f )
7.5×1014 Hz to 3×1016 Hz
X-rays
X-rays have very high energy so exposure to them should be limited since they can damage cells. They are used in CT scans. A CT scan views different angles and combines them into a 3D image.
Wavelength ( λ )
1×10-9 m to 1×10-11 m
Frequency ( f )
3×1016 Hz to 3×1019 Hz
Gamma rays
Gamma rays have the highest energy of all types of electromagnetic radiation. They are produced during nuclear reactions such as those occurring on the sun.
Wavelength ( λ )
1×10-11 m and smaller [to infinity]
Frequency ( f )
3×1019 Hz and higher [to infinity]
Radio
Macrowave
Infrared
Visible
Light
Ultra-
violet
X-Ray
Gamma
Ray
Wavelength & Frequency
Energy
